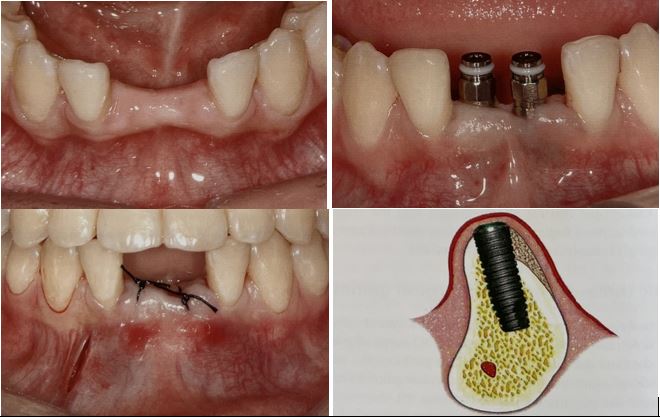
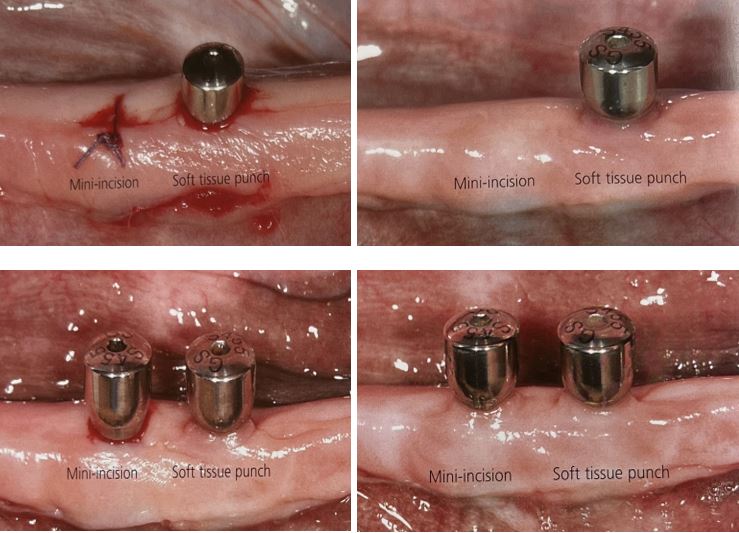
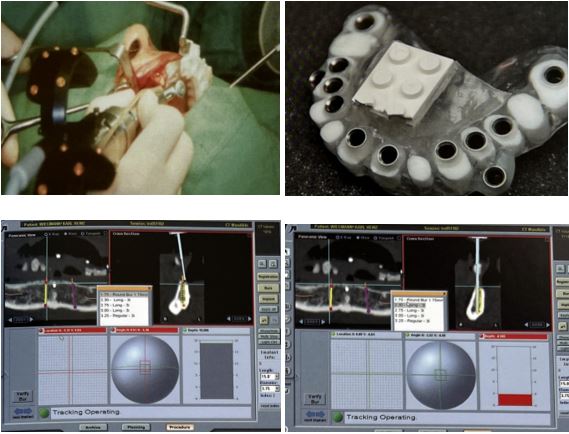
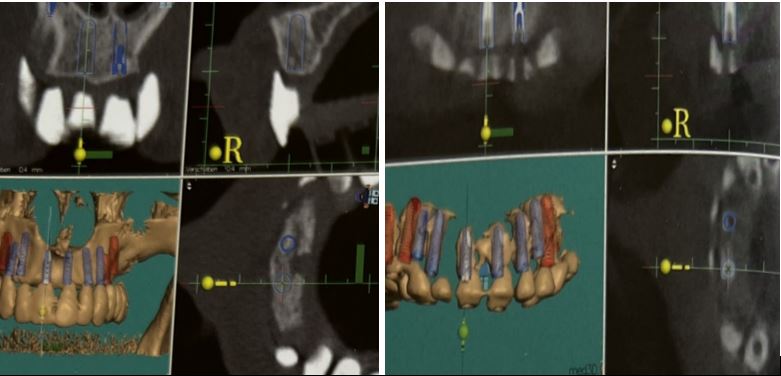
Treatment planning in implantology Classification of osseous defects related to gingival architecture
Deformities found in the alveolar ridge can be attributed to congenital and developmental factors, tooth loss, accidents, unsuccessful endodontic treatment, trauma, advanced periodontal disease, odontogenic cysts or tumors, traumatic tooth extraction, dehiscence or fenestration, and prolonged use of a tissue-supported removable partial prosthesis or complete dentures.
According to the literature, 90% of alveolar ridge deformities are due to premature tooth loss. The residual ridge resorption has been described in the literature by several authors.
The alveolar ridge looses much of its volume in the first year after tooth extraction (25%), reaching up to 40% after three years.
Over the last 15 years, several attempts have been made to treat the alveolar ridge deficiencies in the esthetic zone: guided bone regeneration (GBR) with a barrier membrane with or without titanium reinforcement, onlay bone grafts, block bone grafts with membrane, particulated bone grafts, autogenous bone grafts from intra/extra oral sites (iliac crest, cranial vault, oral cavity), freeze dried demineralized bone allograft, and more recently the alveolar distraction osteogenesis technique.
Also, studies shown that vertical ridge augmentation has a poorer prognosis than the horizontal ridge augmentation.
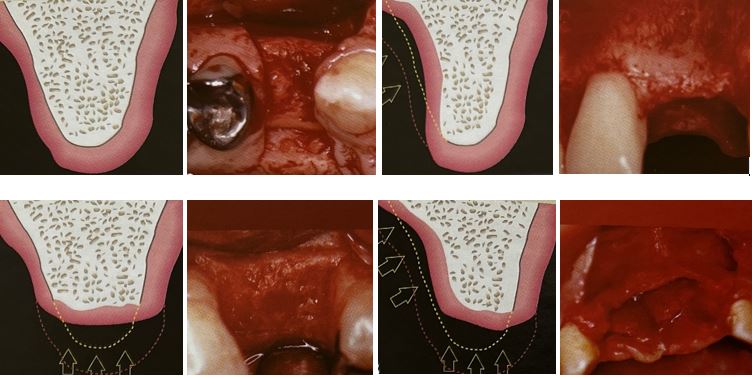
برنامه ریزی درمانی در ایمپلنتولوژی طبقه بندی نقایص استخوانی مرتبط با معماری لثه
ناهنجاری های یافت شده در برجستگی آلوئولی را می توان به عوامل مادرزادی و رشدی، از دست دادن دندان، تصادفات، درمان ناموفق ریشه، تروما، بیماری پیشرفته پریودنتال، کیست ها یا تومورهای ادنتوژنیک، کشیدن دندان تروماتیک، کنده شدن یا بند آمدن دندان، و استفاده طولانی مدت از بافت نسبت داد. پروتز متحرک جزئی یا پروتز کامل.
بر اساس متون، 90 درصد ناهنجاری های ریج آلوئولی به دلیل از دست دادن زودرس دندان است. تحلیل برآمدگی باقیمانده در ادبیات توسط چندین نویسنده توضیح داده شده است.
برجستگی آلوئولی در سال اول پس از کشیدن دندان (25%) حجم زیادی از حجم خود را از دست می دهد و پس از سه سال به 40% می رسد.
در طی 15 سال گذشته، چندین تلاش برای درمان نواقص برآمدگی آلوئولی در ناحیه زیبایی صورت گرفته است: بازسازی استخوان هدایت شده (GBR) با یک غشای مانع با یا بدون تقویت کننده تیتانیوم، پیوند استخوان روی پیوند، پیوند استخوان با غشاء، استخوان ذرهای. گرافت، پیوند استخوان اتوژن از محل های داخل/خارج دهانی (ایلیاک تاج، طاق جمجمه، حفره دهان)، آلوگرافت استخوان دمینرالیزه خشک شده با انجماد، و اخیراً تکنیک استخوان سازی حواس پرتی آلوئولی.
همچنین، مطالعات نشان داده است که افزایش برجستگی عمودی پیش آگهی ضعیف تری نسبت به تقویت برجستگی افقی دارد.
مجموعه درین کاشت مانا به عنوان بزرگترین تولید کننده ایمپلنت های دندانی در ایران، این افتخار را دارد تا با تولید محصولات باکیفیت از مواد اولیه درجه یک و مطابق با استاندارد های روز دنیا، گامی بلند در جهت خودکفایی کشور در زمینه تولید انواع ایمپلنت های دندانی برداشته و محصولات خود را با بهترین قیمت در اختیار دندانپزشکان و مصرف کنندگان قرار می دهد.
جهت کسب اطلاعات بیشتر و ثبت سفارش از طریق این لینک وارد فروشگاه شوید و یا از طریق راه های ارتباطی مجموعه با کارشناسان ما در تماس باشید.
درین کاشت مانا بزرگترین تولید کننده ایمپلنت های دندانی در ایران
جهت خرید ایمپلنت های ایرانی 3A با این شماره تماس بگیرید.
شماره تماس : 02126855680
شماره تماس : 09120383407