گروه علمی شرکت درین کاشت مانا تقدیم می کند
Flapless implantology Three-dimensional planning based on CT or DVT
Part 2
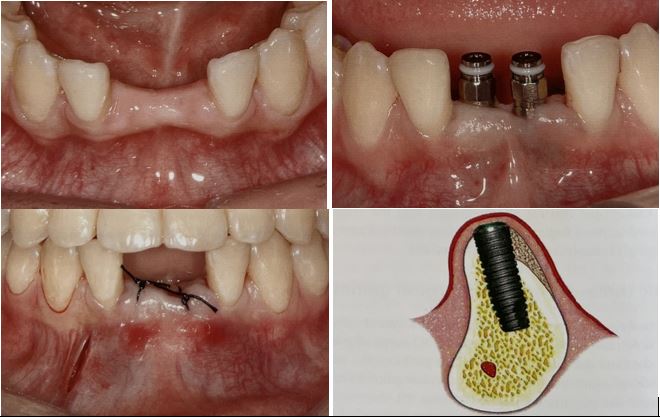
Diagnostic templates consist of radiopaque artificial teeth or may have gutta-percha radiopaque cylinders that the patient wears during the CT examination. These templates enable the dentist to evaluate available bone height at the proposed implant sites.
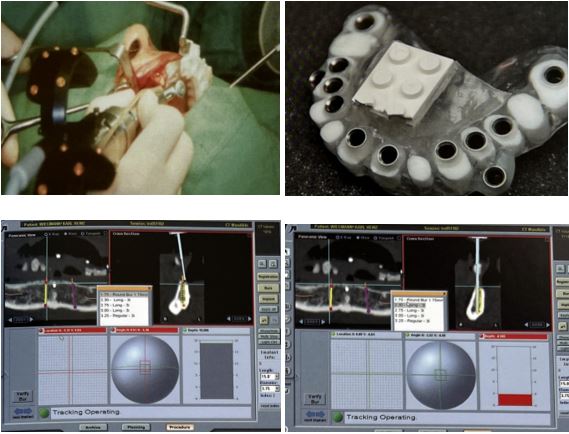
The cross-sectional view of the CT scan allows the clinician to determine implant size, length, and angulation.
When bone augmentation in the maxillary sinus is needed to place implants, CT scanning of the sinus may be used to estimate the amount of graft material required for the ideal volume of sinus graft material.
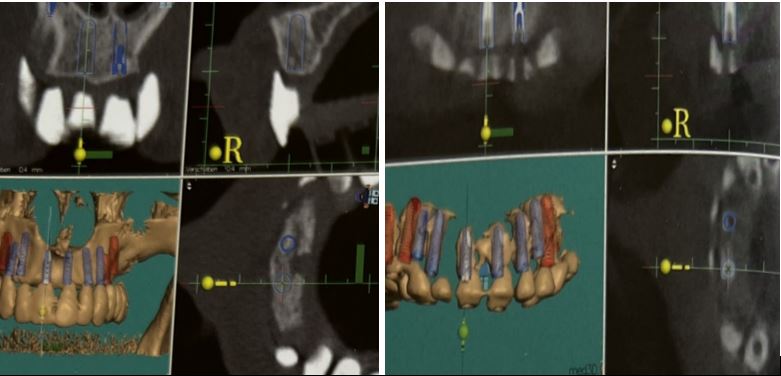
A 3D evaluation of the implant’s proximity to vital structures can also be done. However, CT scanning is expensive, which can be a disadvantage.
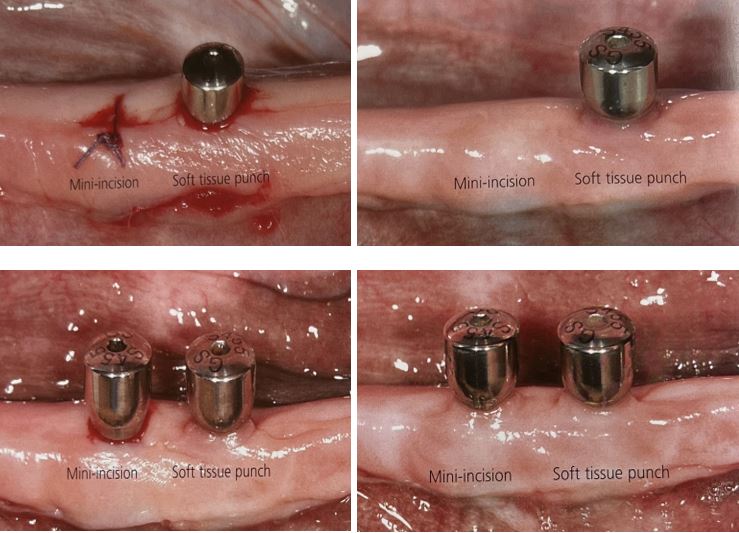
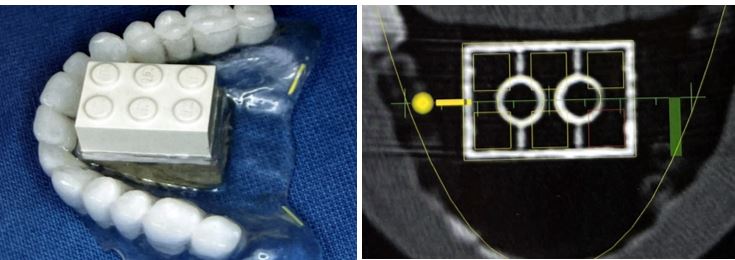
Radiographic splints serve as a reference while 3D imaging data are being taken. Splints may use reference bodies and provide obligatory radiopaque crowns, which are needed for the alignment of the implants. Radiographic splints do not contain any guiding elements for implants. To guarantee a perfect anatomical fit of the splint in situ, radiographic splints are important.
This may be difficult in edentulous patients, particularly in the mandible. Therefore, stabilizing pins or temporary implants may be used. Any unining pins to temporary implants may be used. Any unintended relative movement of the radiographic splint during the radiographic evaluation can directly lead to erroneous planning and, therefore, counteracts the precision provided by the method.
Flapless implantology Three-dimensional planning based on CT or DVT
ایمپلنتولوژی بدون فلپ برنامه ریزی سه بعدی بر اساس CT یا DVT
قالبهای تشخیصی شامل دندانهای مصنوعی رادیوپاک یا ممکن است دارای استوانههای رادیوپاک گوتاپرکا باشند که بیمار در طول معاینه CT از آن استفاده میکند. این قالب ها دندانپزشک را قادر می سازد تا ارتفاع استخوان موجود در محل های ایمپلنت پیشنهادی را ارزیابی کند.
نمای مقطعی سی تی اسکن به پزشک اجازه می دهد تا اندازه، طول و زاویه ایمپلنت را تعیین کند.
هنگامی که برای کاشت ایمپلنت نیاز به تقویت استخوان در سینوس ماگزیلاری است، سی تی اسکن سینوس ممکن است برای تخمین مقدار مواد پیوند مورد نیاز برای حجم ایده آل مواد پیوند سینوس استفاده شود.
یک ارزیابی سه بعدی از نزدیکی ایمپلنت به ساختارهای حیاتی نیز می تواند انجام شود. با این حال، سی تی اسکن گران است، که می تواند یک نقطه ضعف باشد.
اسپلینت های رادیوگرافی به عنوان مرجع در حین گرفتن داده های تصویربرداری سه بعدی عمل می کنند. اسپلینتها ممکن است از بدنههای مرجع استفاده کنند و روکشهای پرتوپاک اجباری را که برای تراز ایمپلنتها مورد نیاز است، تهیه کنند. اسپلینت های رادیوگرافی حاوی هیچ عنصر هدایت کننده ای برای ایمپلنت نیستند. برای تضمین تناسب کامل آناتومیکی اسپلینت در محل، اسپلینت های رادیوگرافی مهم هستند.
این ممکن است در بیماران بی دندانی، به ویژه در فک پایین، دشوار باشد. بنابراین، ممکن است از پین های تثبیت کننده یا ایمپلنت های موقت استفاده شود. می توان از هر گونه پین های جداکننده ایمپلنت های موقت استفاده کرد. هر گونه حرکت نسبی ناخواسته اسپلینت رادیوگرافی در طول ارزیابی رادیوگرافی می تواند مستقیماً منجر به برنامه ریزی اشتباه شود و بنابراین با دقت ارائه شده توسط روش مقابله می کند.